Origins
On 31 March 1492, the Spain of three religions (Christianity,
Islam and Judaism) followed the example of other European nations.
After the fall of Grenada, which marked the end of the Reconquista,
the Catholic monarchs, Ferdinand and Isabella, decided to expel
those Jews who refused to convert to Catholicism.
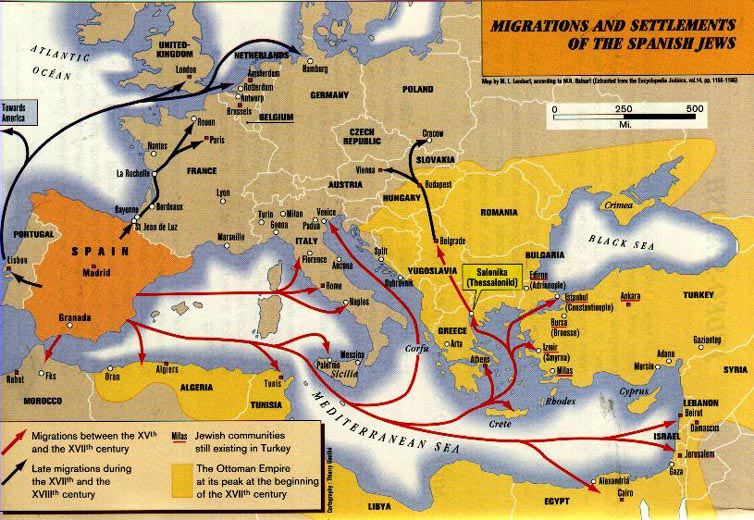
The nearly 200,000 Spanish Jews who went into exile in Portugal,
northern Europe and the entire Mediterranean basin were called
Sepharades or Sephardim, based on the Hebrew name for Spain, Sepharad
(these words have at times been written alternatively with "f"
rather than "ph").
Top of page
Migrations of the Spanish Jews
In general, the Spanish Jews integrated into existing Jewish communities
and adopted their language after a certain time. However, in the
north of Morocco and in the nascent Ottoman Empire they retained
their Spanish language and imposed it on the resident Jews, and
even non-Jewish communities used the language in trade relations.
However, the culture and language of the Spanish Jews was to follow
a new path. As it evolved outside Spain, the archaic 15th century
Castilian was soon considered to be specifically Jewish. From
this came the name Judeo-Spanish, which is used in this text with
its accepted linguistic meaning.
Top of page
Top of page
Before the Second World War and shortly thereafter, communities
of Spanish Jews still banded together in northern Europe (France,
England, Belgium, the Netherlands, etc.) under the name Sephardim
or Sepharades, but an excessively simplistic dichotomy divided
Judaism into two branches. In contrast to the Ashkenazi Jews who
spoke Yiddish or Judeo-German, and confusing rites with ethnic
origin, any Jew who was not an Ashkenazi came to be called a Sephardi,
whether he spoke Spanish, Arabic, Iranian, Greek or any other
language subsequently acquired (while, for example, Roman Catholics
are not all necessarily Italian!). This was the result of recent
changes such as new migrations due to the phenomenon of decolonisation.
This is the case of north African Jews who use the Sephardic rites
but are not of Sephardic origin. Thus, the content has changed
but the label remains the same. In contrast, the Jews of Rhodes
who settled in the Congo/Zaire and later in Belgium are truly
of Sephardic origin.
For the purpose of this publication, the term Sephardim will be
used when speaking of the Judeo-Spanish speakers. This covers
all Jews from northern Morocco and from the former Ottoman Empire,
including their present-day descendants who are dispersed to the
four corners of the earth. These people are helping to preserve
the Spanish of 1492, or at least the Judeo-Spanish vernacular
which sprang from it. We also include those who adopted this language
by integrating into Judeo-Spanish communities.
Therefore, it is to those Jews who so "miraculously" preserved
their language and culture for more than four centuries, to their
slow agony during the dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire, to
their fate and to their brutal death under the steamroller of
the Nazi regime, that these pages are dedicated.
Top of page
Judeo-Spanish, a language of fusion and a living museum for 15th
century Spanish
According to the linguist B. Pottier, when the Jews were expelled
from Spain in 1492, they took with them the varieties of Spanish
- Leonese, Aragonese and especially Castilian (the language of
the Court) - that were common to those who practised the country's
three religions. These form the substratum of that which, around
1620, would become the Judeo-Spanish vernacular, known as Spaniol,
Judezmo, Judy¢, Jidy¢ (according to Edgard Morin), Spaniolith
(Spaniolish for the Nobel Prize winner Elias Canetti) or Espanioliko
in the Middle East, Haketiya in northern Morocco or Tetuani in
the region around Oran in Algeria. All of these terms designate
the Judeo-Spanish vernacular, which would in turn also evolve.
We say around 1620, because the process by which travellers from
Spain stopped being able to understand the ancestor of their language
in the Spanish spoken by the descendants of those they had expelled
was a gradual one and attributed Jewishness to these people. Similarly,
the Muslim Turks who knew Spanish only via the Jewish minority
called the language Yahudije (Yahudice means "Jewish" in Turkish).
Thus, by means of a historical mistranslation, the Spanish Jews'
language became their identifier. Judy¢ (Jew) designates both
the language (the Judeo-Spanish vernacular) and the speaker of
Judeo-Spanish (the Sepharad), as is the case with Yiddish (Ger.,
J?disch meaning Jew) for the Ashkenazim. By means of a similar
mistranslation, we would have probably attributed a Judeo-French
language to the French Canadians if they had been Jews! This is
absurd, and yet the name Judeo-Spanish has stuck.
Judeo-Spanish, a language of fusion, is essentially 15th century
Castilian, coloured initially by regionalisms and hispanic Arabicisms,
and after 1492 by Moroccan Arabicisms, Turkisms, Italianisms,
Hellenisms, Slavisms, etc. taken on in the various host countries.
Later, with the creation of the schools of the Alliance Isra,lite
Universelle in 1860, the language was affected by a mania for
gallicization, to the point that a new dialect called judeo-fragnol
(Judeo-Franco-Spanish) emerged.
We said in our subtitle that Judeo-Spanish is a living museum
for 15th century Spanish. Indeed, in 1492 - the date of the Jews'
expulsion from Spain - Castilian had not yet undergone the silencing
of voiced sibilants or the birth of the jota. Thus, the intervocalic
[z] of that time remains, and one continued to say [meza] for
mesa, (with [s], "table"). Similarly, one continued to say [ka's'a]
for caja, "box" or "crate," or [pa'z'a] for paja, or "straw."
It is precisely for this reason that Don Quixote [Don Ki's'o-te],
which is now written Don Quijote - with jota - arrived in France
as Don Quichotte, with [ch], reflecting the pronunciation of that
time.
The distinction between [b] and [v] would also be maintained:
[kantava] for cantaba, "I" or "he sang." Other archaic forms also
persisted: kavdal - kovdisya - kovdo - sivda etc., which later
became caudal in Spanish, "goods or fortune," codicia"cupidity
or covetousness," codo "elbow," ciudad "city," etc.
There are also numerous "vulgarisms" from that time: agora - prove
- guevo - guerfano, etc. for ahora, "now," - pobre "poor" - huevo
"egg" - huerfano "orphan." Similarly, the two forms muevo/nuevo
coexist for "new.".
Morphology: The old verbal forms do- vo- so and esto for doy "I
give" voy "I go," soy "I am" and estoy both "I am" in English,
continued to be used. As in the popular Spanish language, the
second person forms of the simple past already had a tendency
to take on a final -s. The metathesis >ld of the imperative form
also continued to be used: kantadlo>kantaldo "sing it."
These observations obviously provide only a few examples illustrating
a much broader topic.
In its subsequent evolution, Judeo-Spanish would develop particularly
interesting strategies for hispanizing various loan words. Thus,
there is continued use of the frequentative verbal ending -ear,
as a verbal hispanizer for all loan words from the Turkish, Arab,
Bulgarian, Greek, etc. host countries (adstrates), except for
those of French origin, which take the -ar ending. Thus, from
the Turkish dayanmak, "resist, endure," we get the Judeo-Spanish
form dayanear. In contrast, based on the French "s'amuser" (to
enjoy oneself), we have the form am?zarse. On the other hand,
the ending -dero, which is very frequent in Spanish, is maintained
but is used especially in forming words for obsessions or habits.
We see this, for example, in the word arraskadero, whose meaning
shifted from "pruritus, itching" to "obsession with scratching."
Vocabulary and semantics (Spanish archaic usages): there are many
examples: merkar (to buy), trokar (to change), mansevez (youth),
etc. The feminine gender of some nouns ending in -oris also kept,
while these have become masculine in standard Spanish.
But along with these archaic usages, which are very understandable
given the historical path of the language, there are also some
genuine lexical creations based on Ladino (Judeo- Spanish calque),
produced by the word-for-word translation from Hebrew into Spanish,
which go back to the 13th or even the 12th centuries. All of these
terms that are more archaic than the vernacular language are,
via the intermediary of Ladino, a faithful reflection of the sacred
languages (Hebrew and Aramaic), which makes them semi-sacred.
By way of example, akunyadar/ear, which means "to fulfil the Levitical
law," (i.e. the obligation found in the law of Moses for the brother
of a dead man to marry the dead man's childless widow).
So, we can see that Judeo-Spanish is a language of fusion. Four
percent of its loan words come from Hebrew, 15 percent from Turkish,
20 percent from French, two percent from Ladino, etc., with all
of these built on the foundation of the 15th century Spanish substratum.
Top of page
Problems of Judeo-Spanish
Ladino is not spoken, rather, it is the product of a word-for-
word translation of Hebrew or Aramaic biblical or liturgical texts
made by rabbis in the Jewish schools of Spain. In these, translations,
a specific Hebrew or Aramaic word always corresponded to the same
Spanish word, as long as no exegetical considerations prevented
this. In short, Ladino is only Hebrew clothed in Spanish, or Spanish
with Hebrew syntax. The famous Ladino translation of the Bible,
the Biblia de Ferrara (1553), provided inspiration for the translation
of numerous Spanish Christian Bibles.
Apart from the phonetic, morphological and syntactic differences
mentioned above (which are very rare, especially in the romances
and proverbs), the spoken language, Judezmo (the Judeo-Spanish
vernacular) does not differ much from peninsular Spanish. However,
as mentioned above, Ladino faithfully reflects the sacred languages
(Hebrew and Aramaic), making it semi-sacred.
Top of page
Spelling
In Spain, two alphabets were used, the Latin and the Hebrew. The
Ladino of the Ferrara Bible was written in Gothic-style Latin
characters for the Marranos of Spain, who returned to Judaism
but knew no Hebrew. Around 1928 in Turkey, at the behest of the
new republican power of Mustapha Kemal Pasha, Latin script replaced
the Hebrew script. However, for quite some time the elders used
Solitreo, Hebrew manuscript writing, which even served as a secret
form of writing in the Nazi concentration camps.
Today, Sephardim write their language according to the alphabet
used in their country. In this text, we use the French- influenced
spelling of the Paris-based Association Vidas Largas for the Defence
and Promotion of the Judeo-Spanish Language and Culture.
Top of page
Old Judeo-Spanish literature (through 1850)
There are essentially two types: liturgical and secular.
The old liturgical literature (Bibles, prayer books etc.) was
written in Ladino, both in the East and the West (Morocco, Bordeaux,
Amsterdam, etc.). It was not until 1730 that texts were written
in Judezmo, notably the famous "Me'Am Lo'ez," a popular 18-volume
encyclopedia published between 1730 and 1908. Secular literature
was passed on mainly in oral form: proverbs, romances, "kantigas,"
tales and fables - all forms which began by perpetuating the Hispanic
heritage and then took inspiration from daily life in the Ottoman
Empire and northern Morocco.
The numerous proverbs are an inexhaustible source of linguistic
and cultural interest; thus, it is not surprising that they are
the subject of studies and investigation, notably at the Arias
Montano Institute in Madrid.
The Sephardic "romancero" - which celebrates more or less recent
events, like the execution in Fez in 1820 of Sol Hachuel, a young
Jewish woman who refused to convert, or the "Gran fuego," a terrible
fire that devastated Salonika in 1912 - has been particularly
long-lived.
This oral literature is of considerable importance for Spain as
well, because through it one has access to aspects of the country
which seemed to have been lost forever. The Jews, faithful to
their ungrateful homeland, have conserved this Spanish of old
in their living museum.
Top of page
Modern literature (1850 to the present)
There has been a progressive westernization of the Sephardic communities
under the combined influence of the schools created by the Alliance
Isra,lite Universelle (52 schools in European Turkey alone) and
the press (more than 300 newspaper and magazine titles). This
has resulted in a new intelligentsia that is westernized, gallicized
and secularized to some extent and has ushered in new literary
genres such as theatre and secular poetry, novels and numerous
translations/adaptations of European works.
The French language became increasingly invasive (notably through
teaching), resulting in a new form of the language in the Ottoman
Empire - Judeo-Franco-Spanish, as mentioned above.
According to Michael Molho, starting in Istanbul in 1832, the
two modes of Judeo-Spanish (Ladino and the vernacular language)
have given rise to a significant body of literature: 5,000 to
6,000 works, not including the 300 press titles which then flourished.
Hundreds of plays have also been discovered since that time.
Top of page
The fate of the Judeo-Spanish - Dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire
The slow dismembering of the Ottoman Empire began in 1699, with
the breaking off of Hungary and Transylvania, and ended with the
proclamation of the Turkish Republic by Ataturk in 1923. This
systematic erosion was aided and abetted by a host of minor interests,
including viziers, pashas and partisans of various strains of
nascent nationalism, as well as the major powers - Austria-Hungary,
Russia, France, England - as they knotted and unknotted their
alliances, and recently unified nations like Germany and Italy.
The Turkish minorities, or millets - Greeks, Armenians, Jews,
etc. - within this veritable republic of nations, were courted
by the West. Each State created its own schools. This contributed
to the Judeo-Spanish emigrating from both the Levant and in Morocco
to Europe and the Americas starting in the end of the 19th century.
Wave followed wave until 1939, and longer for Morocco.
Top of page
Lost unity
Within the Ottoman bloc there was a united Judeo-Spanish bloc,
for which the cities of Salonika, Kavalla, Adrianople, Constantinople,
Smyrna, Sofia, Sarajevo, Jerusalem, Safed, Alexandria and Cairo
served as guiding lights. Rabbis and advisors were sought there
by the entire Sephardic world: Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Antwerp,
Brussels, Paris, Corfu, London, Venice, Milan, Livorno, Hamburg,
Altona, Buenos Aires, Mexico City, New York, Miami, Santiago de
Chile, etc.
The dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire brought the disintegration
of this bloc. Spanish Judaism had lost its glue. Sephardim again
went into exile. In their new host countries, they were faithful
to their language and established religious and ethnic communities.
One international magazine, Le Judaïsme Séphardi, served as their
link. However, in 1948, in the United States, the last Judeo-
Spanish newspaper printed in Hebrew characters, La Vara, stopped
being published.
Top of page
The Holocaust, 1939-1940 - A language assassinated
World War II and the Holocaust with its genocide would soon decimate
the Judeo-Spanish population:
* In Greece, there were 79,950 in 1940 but only 10,371 in 1947.
Thus, more than 50,000 Sephardim perished there.
* In Yugoslavia, there were 71,000 in 1940 but only 14,000 survivors
in 1944, of which 8,000 were authorised to emigrate to Israel.
55,000 Sephardim perished in Yugoslavia.
* In Romania, at least 15,000 Sephardim perished.
* In Bulgaria, there were 40,000 in 1940 and 50,000 in 1947. No
Jews were deported from Bulgaria thanks to the Bulgarian people's
fierce opposition to the extermination of their Jewish compatriots.
In 1949, only 9,700 were left, the others having emigrated to
Israel, where their melodious language can still be heard today
in the streets of Tel Aviv and Bat Yam in particular.
In addition to these victims, there are the Sephardim who emigrated
within Europe, where the Nazi occupation took them by surprise.
60,000 perished. In all, around 160,000 Sephardim perished out
of the 365,000 counted in 1925. The Sephardim of Morocco were
protected, but left the country en masse during the decolonisation
process.
Top of page
The Sephardim today
Their numbers are, of necessity, approximate, 378,000 in all,
broken down as follows: Israel - 300,000; Bulgaria - 3,000; Turkey
- 15,000; northern Morocco - 3,000; New York and the US in general
- 15,000; Greece - 2,000; France, Belgium and England - 40,000.
This trend continues, because although the number of those who
acknowledge Judeo-hispanicity is probably much higher (we are
thinking here of Jews in Latin American countries, where the number
of those who still speak their language of origin is dropping
quickly). Moreover, all or nearly all are bi- or tri- lingual.
In Israel, the last major reservoir of Sephardim, the understandable
hebraization is also undermining the presence of Judeo-Spanish.
The only magazine still written entirely in this language, Aki
Yerushalayim, is a sort of symbol for all of the nostalgia concerning
Judeo-Spanish throughout the world. In the Turkish weekly alom,
only one page in between six and ten is in Judeo-Spanish. These
are the two survivors of a once- thriving press that boasted over
300 titles.
Top of page
A renaissance for Judeo-Spanish through its literature
For more than 30 years, Judeo-Spanish literature, both prose and
poetry, has been blossoming. Examples are "En torno de la Torre
blanca," a moving chronicle set in Salonika by the novelist Enrique
Saporta y Beja, and "Elsekreto del mundo" by Itzak Ben- Rubi,
which brings the world of the concentration camp to life. Poets
include Clarisse Nicoidski, who writes novels in French and poems
in the language closest to her heart, Balkan Judeo-Spanish, Salamon
Bidjerano and his "Kantes de Maturidad," and Lina Albukrek, the
author of delicious poems that were faithfully compiled by her
daughter in a book entitled "87 anios lo ke tengo."
We should add to this all-too-brief list all of those who compiled
tales, proverbs and romances, thus helping to safeguard this precious
heritage. They include Israeli Matilda Koen- Safrano's compilation
entitled "Kuentos del folklor de la Famiya Djudeo-espanyola" and
Jaime B. Rosa's book entitled "Sepharad 92," which contains a
collection of poems by Avner Perez, Izan Konorti, Isahar Avzaradel,
etc.
Finally, there are works in other languages which keep the memory
of Judeo-Spanish alive. Some of these include Annie Benveniste's
chronicle "Le Bosphore ? la Roquette," Brigitte Peskine's "Les
eaux douces d'Europe" and Nelly Kafsky's "Le rêve d'Esther," which
was adapted very successfully for television.
Top of page
Judeo-Spanish in universities
Today, attempts are being made to recover the remains of this
culture. Universities have become involved in this, and the number
of teaching posts for Judeo-Spanish (language, culture and civilization)
are increasing throughout the world. The first was created in
Paris - at the Ecole des Langues et Civilisations Orientales Vivantes
- in 1967, and the Sorbonne (Institut d'Etudes Hispaniques) and
the Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes followed suit. The Université
Libre de Bruxelles (Institut Martin Buber) did the same in 1972.
In these establishments, where H.V. Sephiha teaches, more than
400 master's and doctoral theses have been written on this discipline,
which the author calls Judeo-hispanology.
Judeo-Spanish is also studied in conjunction with the study of
dialects in all linguistic courses in Hispanic or Iberian faculties
in French universities.
The same goes for universities in Spain, where the Arias Montano
Institute in Madrid has published the magazine Sefarad since 1941,
which is to Judeo-Spanish what the magazine Al-Andalus is to Spanish
Islam.
In Germany and other European countries, Judeo-Spanish is taught
in the Romance language department of universities. One example
is the Institut f?r romanische Philologie of the Freie Universit?t
of Berlin. Judeo-Spanish is also a topic of interest at the universities
of T?bingen, Munich, Trier, Aachen, and Frankfurt, and in Innsbruck
in Austria, in Fribourg, Neuchftel and Geneva in Switzerland,
and in the Spanish language departments of the universities of
Venice and Padua. Other universities also touch on the subject
in their departments of Iberian or Hebrew studies. Hispanic studies
departments in England are interested in Judeo-Spanish as well.
Numerous university correspondents in the above mentioned countries
as well as Greece, Poland, former Czechoslovakia, Hungary, the
former USSR, Bulgaria, Romania, former Yugoslavia, Denmark, the
Netherlands, Sweden and Norway have announced the creation of
teaching and research centres for this discipline. This shows
the importance that is attributed to it.
In Israel, after a certain rejection of the languages of the Diaspora,
awareness began to grow regarding the linguistic and cultural
wealth of Judeo-Spanish. At present, this discipline is taught
in most Israeli universities.
In addition to the Judeo-Spanish language, the literature and,
in particular, the Judeo-Spanish romancero are drawing the attention
of specialists in Spanish literature in universities in France
and abroad. An example of this is the recent bilingual anthology
of Spanish poetry by La Pl,iade and the production of many records
of Judeo-Spanish songs over the last three decades.
Top of page
Community education and life
Community education is also important. In France, the Vidas Largas
Association for the Defence and Promotion of the Judeo- Spanish
Language and Culture was created in 1979, making it possible to
bring Judeo-Spanish instruction into the Communities of Paris,
Marseille and Lyon. Similar things are happening in the context
of the association Los Muestros (http://www.sefarad.org/) in Belgium
and throughout the world. And finally, the magazine Aki Yerushalayimis
already available on the Internet at the following address: http://www.trendline.co.il/judeospa/.
There has also been a great revival of interest in Judeo-Spanish
culture. Examples are the many magazines and bulletins being published
throughout the world. There is also evidence of this cultural
renaissance on the radio, with daily broadcasts in Israel and
Madrid, a bi-weekly programme in France and a weekly programme
in Belgium.
Top of page
The future of Judeo-Spanish
All of the above is very encouraging. Death throes have given
way to rebirth. However today, while parents attend to their lucrative
occupations, it is often the grandparents who introduce the children
to Judeo-Spanish and instill in them an interest in their past.
The message is getting across, and this trend appears to be irreversible,
but we must continue to consolidate and protect the heritage of
the ancients. It is to this end that Judeo-Spanish workshops are
being created everywhere, in collaboration with a growing number
of researchers.
Top of page
Associations, magazines, and periodicals
- Vidas Largas, Association and Magazine for the Defence and Promotion
of the Judeo-Spanish Language and Culture: 37, rue Esquirol, 75013
Paris. This association has three branches: in Marseille, Lyon
and Geneva.
- France Mabatt, Association of Sephardim from northern Morocco:
c/o J. Pimienta, 128, rue Legendre, 75017 Paris.
- Nouvelles de l'Institut d'Etudes du Judaïsme, U.L.B., Bruxelles.
- Los Muestros, La boz de los Sefaradim - La voix des Sépharades
- The Sephardic Voice: 66, avenue de Messidor - 1180 Bruxelles.
- Sefarad, Institut Arias Montano: CSIC, Medinaceli, 4 - Madrid
14.
- Annual (Godichnik): Social and cultural organisation of Bulgarian
Jews: 50 boulevard Stamboliisky, Sofia.
- Erencia (Etats-Unis).
- Aki Yerushalayim, Jérusalem - in Judeo-Spanish only - P.O. Box
1082 Jerusalem.
- Shalom, Istanbul, weekly in Turkish, 1/6 in Judeo-Spanish.
- Jevrejski Pregled, Federation of Jewish Communities of Yugoslavia:
Ul. 7 jula, 71a post, fah 881, Belgrade.
- Israelite Community of Thessaloniki: 24, Tsimiski St., Thessaloniki.
- World Sephardi Federation: 67/8, Hatton Garden - London.
Bibliographie succincte
- BUSSE, W., Hommage à Haïm Vidal Sephiha, in Sephardica, Peter
Lang, exhaustive bibliography of H.V. Sephiha, pp. 21-63. 1996.
- DIAZ-MAS, P., Los Sefardies, Historia, lengua y cultura. Riopiedras
Ediciones. 1986.
- KOEN-SARANO, M., Kuentos del folklor de la famiya djudeo-espanyola,
in Judeo-Spanish and Hebrew. Ed. Kana, Jérusalem 1986.
- HASSAN, J.M. & ROMERO, E. (ed), Actas del Primer Simposio de Estudios
Sefardies. C.S.I.C., Madrid 1970.
- LEROY, B., L'Aventure séfarade, de la péninsule ibérique à la
diaspora. Albin Michel, Paris 1986.
- RENARD, R., Sepharad. Annales de l'Université de Mons, Mons 1966.
- SACHAR, H.M., Adios España, Historia de los Sefardies. Thassalia
1995.
- SEPHIHA, H.V., L'agonie des Judéo-Espagnols. Ed. Entente, "Minorités"
collection, Paris 1977, 1979 et 1991 (with a chapter on the Judeo-Spanish
press).
- SEPHIHA, H.V., Le judéo-espagnol. Ed. Entente, "Langues en péril"
collection, Paris 1986.
- SEPHIHA, H.V., Contes judéo-espagnols - Du miel au fiel. Translated
and presented by H.V. Sephiha. Ed. Bibliophane, Paris 1992.
To obtain a more complete bibliography, including records and
videos, contact:
Association VIDAS LARGAS
37, rue Esquirol
F-75 013 Paris
Institut Sépharade Européen
avenue de Messidor 66
B-1180 Bruxelles
e-mail: moise.rahmani@sefarad.org
Top of page
|
![]() Judeo-Spanish at Auschwitz - Le judéo-espagnol à Auschwitz -
El Judeo-español en Auschwitz
Judeo-Spanish at Auschwitz - Le judéo-espagnol à Auschwitz -
El Judeo-español en Auschwitz 